- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-16 Origin: Site








Choosing the right network cable can make or break your system’s performance. Shielded vs. unshielded cables—which one is better for your setup? This choice is more than just about cost; it affects your network’s reliability and longevity.
In this article, we'll explore the key differences between shielded vs. unshielded cables, the environments where each type excels, and how to make the best decision based on your needs. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of what works best for your network.
Shielded cables (also known as Shielded Twisted Pair cables, or STP) are Ethernet cables that come with additional layers of protection to reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference (EMI). The main purpose of shielding is to protect the data being transmitted over the cable, ensuring that external signals do not degrade the quality of the network communication.
The shield can be made from a variety of materials, such as foil, braided copper, or even a combination of both. This additional layer can protect the internal wiring from interference that might otherwise lead to data loss or slower transmission rates. In environments with a lot of electrical equipment, the shielded cable ensures that data integrity is preserved.
Not all shielded cables are the same. There are several types designed for different levels of protection against EMI:
1. Foil-shielded Cables (F/UTP): This type of shielding involves a foil wrap around the entire cable. While it offers basic protection against EMI, it is less durable and more susceptible to physical damage over time.
2. Braided Shielded Cables (S/UTP): These cables use a braided copper shield around the entire cable. Although they offer more durability compared to foil shields, they still provide moderate protection against EMI.
3. Foil and Braided Shielded Cables (SF/UTP, F/FTP): These cables combine foil and braided shields around the cable and the twisted pairs inside. This provides the highest level of protection, making them ideal for high-traffic, high-EMI environments such as industrial settings, data centers, and medical facilities.
Unshielded cables (also known as Unshielded Twisted Pair cables, or UTP) are simpler Ethernet cables that do not have additional shielding. While they still have twisted pairs of wires, there is no protective layer to prevent interference. This means that UTP cables are more vulnerable to electromagnetic interference, especially in environments where a lot of electrical equipment is running.
Despite lacking additional shielding, unshielded cables can still perform well under certain conditions, especially in quieter environments where EMI is minimal. The absence of shielding makes these cables more flexible, lightweight, and easier to install.
Unshielded cables are primarily used in environments where interference is minimal. Some common use cases include:
1. Home networks: Since most home environments do not have high levels of EMI, UTP cables can efficiently handle the typical data traffic of a household.
2. Small office networks: Smaller offices with low-density networking needs can also benefit from the cost-effectiveness and ease of installation provided by UTP cables.
3. Short-range installations: Unshielded cables are ideal for networks that don’t require long cable runs or high-speed data transfer. They are often used in simpler setups where the risk of interference is low.
One of the most significant differences between shielded vs. unshielded cables lies in their ability to handle electromagnetic interference (EMI):
● Shielded cables provide superior protection against EMI, ensuring the integrity of data transmission in environments where electronic interference is common. This makes them ideal for environments such as factories, data centers, or hospitals where many machines and devices may interfere with network performance.
● Unshielded cables, on the other hand, offer limited protection against EMI. While they can work well in quieter settings, they are more prone to signal degradation in environments with heavy electrical equipment. If you're working in a location where EMI is a concern, shielded cables are often the better choice.
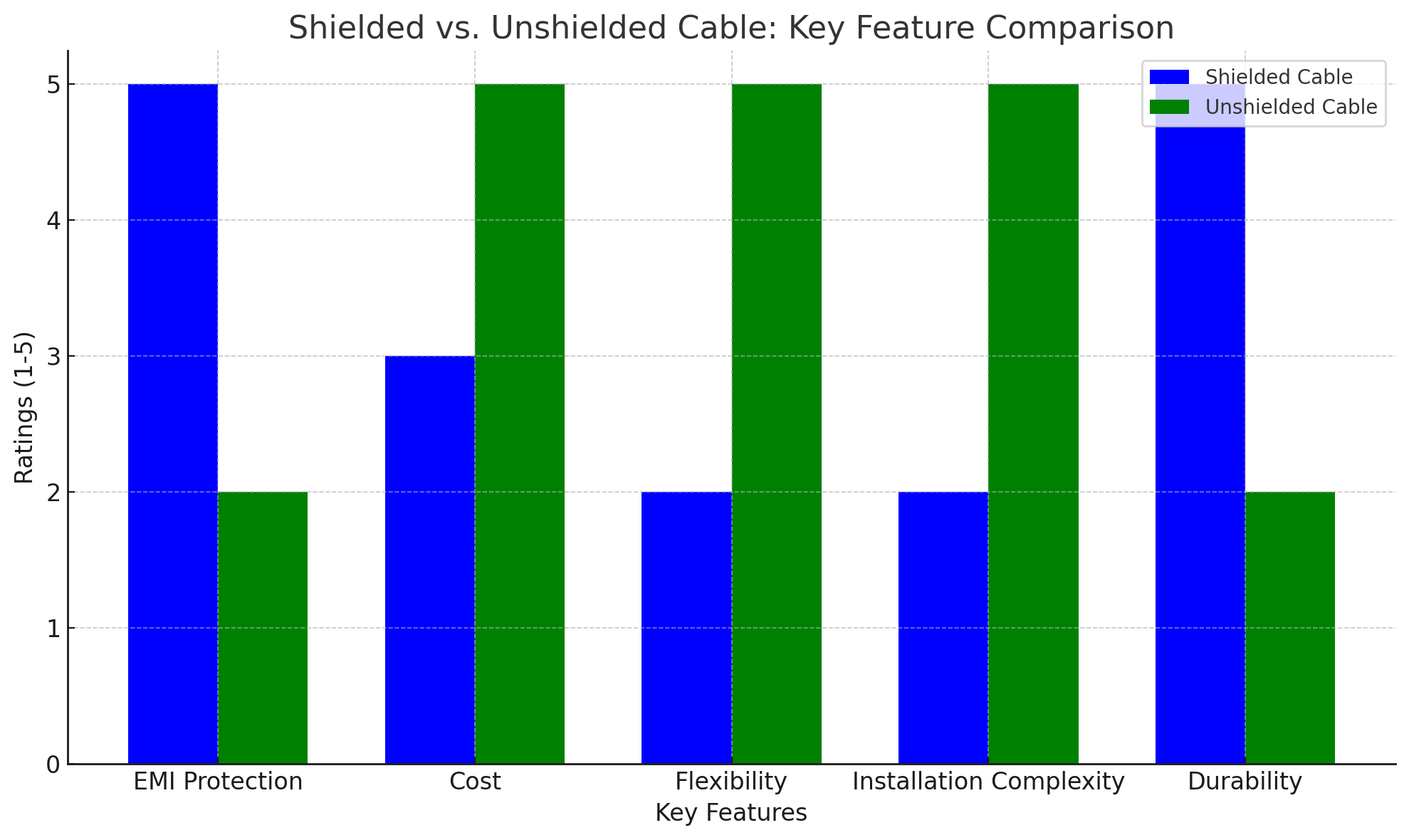
Feature | Shielded Cable (STP) | Unshielded Cable (UTP) |
EMI Protection | High protection against EMI | Minimal protection against EMI |
Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
Flexibility | Less flexible, stiffer construction | More flexible, easier to manage |
Installation Complexity | More complex, requires grounding | Easier to install, no grounding required |
Durability | More resistant to environmental factors | Less resistant to external factors |
When it comes to cost and installation, shielded cables and unshielded cables differ significantly:
● Shielded cables are more expensive due to the additional materials required for the shielding. They are also more difficult to install because they are stiffer and bulkier than unshielded cables. Proper grounding and additional hardware may be needed for optimal performance, which further increases the installation complexity and cost.
● Unshielded cables are generally much more affordable. They are easier and faster to install, as they are more flexible and lighter. These cables are often the go-to choice for budget-conscious projects or smaller network setups where EMI is not a significant issue.
● Shielded cables are more durable and resistant to physical damage, such as moisture or abrasion. However, their construction makes them less flexible. They are harder to manage and install, especially in tight spaces or when routing through conduits.
● Unshielded cables are more flexible and lightweight, making them easier to maneuver and install in tight spaces. However, they lack the durability of shielded cables and are more vulnerable to physical damage in harsher environments.
Shielded cables are best suited for environments where electromagnetic interference is a significant concern. Some examples include:
● High-traffic networks: Large office buildings, factories, and data centers that handle large amounts of data and contain numerous electronic devices prone to creating EMI.
● Electromagnetic interference: Environments with high levels of interference, such as near generators, heavy machinery, or fluorescent lights, where signal integrity must be maintained.
● Outdoor installations: Environments exposed to outdoor elements, such as lightning strikes, require the enhanced protection of shielded cables, often in conjunction with surge protection devices.
Cable Type | Ideal Environments |
Shielded Cable (STP) | Factories, data centers, environments with heavy machinery, high-traffic networks, or high EMI environments |
Unshielded Cable (UTP) | Home networks, small offices, low-interference environments, short-range installations |
Situation | Shielded Cable (STP) | Unshielded Cable (UTP) |
High EMI environments | Yes, highly recommended | No, not recommended |
Small office or home network | No, unless there is heavy interference | Yes, ideal for simple installations |
Budget-friendly installations | No, higher upfront cost | Yes, more cost-effective |
Large networks or data centers | Yes, essential for optimal performance | No, may cause performance issues |
Unshielded cables are better suited for quieter environments where EMI is minimal:
● Home and small office networks: These environments typically don’t experience high levels of interference, and UTP cables can handle the data transmission requirements effectively.
● Short-range installations: Unshielded cables work well for small-scale network setups or when the cable run does not extend beyond a few meters, where EMI is not a concern.
● Budget-conscious setups: If cost is a key factor and the environment is relatively free from interference, unshielded cables offer an affordable and efficient solution.
Shielded cables offer superior protection against EMI, which helps maintain the integrity of data transmissions. By minimizing the chance of external interference, these cables ensure faster, more reliable data transfer, especially in high-traffic or high-EMI environments.
In addition to their EMI protection, shielded cables are built to withstand harsher environmental conditions. They are more resistant to moisture, abrasions, and physical damage, making them ideal for industrial or outdoor settings.
If you anticipate future growth or need to upgrade your network to handle higher speeds, shielded cables provide a better long-term investment. Their robust construction and EMI protection ensure that your network remains functional and reliable as demands increase.
Advantage | Shielded Cable (STP) | Unshielded Cable (UTP) |
Data Integrity | Ensures high-speed, error-free data transfer | May suffer from interference and data loss |
Durability | More durable, resistant to moisture, abrasion | Less durable but more flexible |
Future-proofing | Ideal for high-performance networks | Best for simple, low-traffic setups |
Cost-effectiveness | Higher initial cost but worth the investment | More affordable, especially for small setups |
One of the main advantages of unshielded cables is their affordability. If you are working with a limited budget, UTP cables can save you money on both the materials and installation costs.
Unshielded cables are easier to install and require less effort to handle. Their lightweight design and flexibility make them ideal for home or small office environments, where installation space may be limited or less critical.
When choosing between shielded vs. unshielded cables, the decision depends on your network's needs. Shielded cables are ideal for environments with heavy traffic and high electromagnetic interference, offering superior data integrity. On the other hand, unshielded cables are a cost-effective solution for smaller, low-interference networks.
OTTO provides a range of high-quality cables to meet both current and future network demands. Their products deliver excellent protection and scalability, ensuring long-term reliability in any setup.
A: Shielded cables offer extra protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for high-traffic or industrial environments. Unshielded cables are more flexible, cost-effective, and work well in low-interference settings.
A: Choose shielded cables for environments with high EMI or heavy equipment. Unshielded cables are suitable for home or small office networks with minimal interference.
A: Yes, shielded cables are generally more expensive due to the added protective layer and grounding requirements, while unshielded cables are more affordable and easier to install.
A: Yes, shielded cables help maintain data integrity by preventing interference, while unshielded cables may experience signal degradation in noisy environments.